Seeing the Light
One of my hopes for the garden railroad is to be able to build some of my own electronics for it. Whether some off-track movement or lights, or a piece of automation that helps manage the trains. It would be very useful to be able to control the automation from the DCC throttle. So there is my starting point: build an Arduino system that listens to DCC and does something with the signal.
After some searching on line I found several options and settled on the basic design from Dave Bodnar at Train Electronics. One of the components needed is an optocoupler. I wasn't familiar with this so did some reading and turns out, this is a pretty ingenious little device. It provides a way to have signals pass from a high voltage part of a circuit (for me DCC running at about 15-18V) to a low voltage part (the Arduino at 3.3 or 5V) while having them electrically isolated. The incoming signal get converted to light (hence to opto-) which is picked up by a photodetector and sent back out. For more details, see Components 101.
This appeared to be a simple enough design that I wanted to try and build a simple one for myself. And I could do it all with basic components I already have. I used it to send Morse code messages between two isolated Arduino boards. See it in operation.
It was a fun little build. But now I have ordered a real one and will start building the DCC decoder. Diagrams and code below for anyone interested.
It is a simple circuit as seen below. I made use of the Lewis library by DefProc. (As a fan of both the Inspector Morse and Inspector Lewis mysteries, I loved reference!)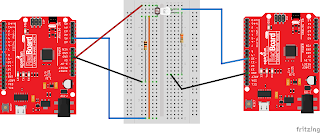 |
| Wiring Diagram |
 |
| Schematic |
Sending Code
* Send Morse code over a home-grown optocoupler.
* This is the send side. See Morse_Code_Receive for the receive side.
* Drives an LED with some frequency and detects it using the photoresistor.
* This is the basic mechanism behind an optocouple or optoisolator.
*
* Sept 9, 2021
* Bryan Barmore
*/
#include <Lewis.h> // Morse code library for encoding and decoding https://github.com/DefProc/lewis/
//#define DEBUG
const int STATUS_PIN = 13;
const int SIGNAL_PIN = 11; //made it PWM so we can play with chaning intesity to see how well that is detected
Lewis Morse; // love the naming!!!!
const int WPM = 40;
String Message = "From here to there ";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //start a serial connection with the computer
pinMode(STATUS_PIN, OUTPUT); //set pin 13 as an output that can be set to HIGH or LOW
digitalWrite(STATUS_PIN, LOW); // turn the light off
pinMode(SIGNAL_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(SIGNAL_PIN, LOW); // turn the light off
Morse.begin(SIGNAL_PIN, SIGNAL_PIN, WPM, false);
}
void loop() {
//Morse.print("l");
morsePrint(Message);
delay (1000);
}
int morsePrint(String message)
{
int messageLength = message.length();
for (int i=0; i<messageLength; i++) {
Morse.print(message[i]);
}
}




Comments
Post a Comment